AI in Cloud Security: Protecting Dynamic Environments
Introduction: The Complexity of Modern Cloud Ecosystems
Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed enterprise IT architecture. Platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) enable organizations to scale infrastructure on demand, deploy global services instantly, and optimize operational costs. However, this elasticity and distributed design introduce significant security challenges.
Unlike traditional static networks, cloud environments are dynamic, API-driven, containerized, and ephemeral. Workloads spin up and down in seconds. Microservices communicate laterally. Infrastructure is defined as code. Misconfigurations, identity abuse, and automated attacks exploit these dynamics.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is emerging as a cornerstone technology for securing these fluid environments. AI-driven cloud security solutions bring automation, predictive analytics, and real-time anomaly detection to environments that are simply too complex for manual oversight.
Why Traditional Cloud Security Approaches Fall Short
Conventional security tools rely heavily on:
-
Signature-based detection
-
Static rule sets
-
Manual configuration reviews
-
Periodic compliance audits
In a cloud-native environment, these approaches become inadequate because:
-
Resources are short-lived and constantly changing.
-
Attack surfaces expand with every new microservice or API endpoint.
-
Human teams cannot monitor millions of logs and events in real time.
-
Zero-day threats bypass signature-based defenses.
AI addresses these limitations by enabling adaptive, behavior-based security models.
AI-Powered Threat Detection in Cloud Environments
Behavioral Analytics and Anomaly Detection
AI systems use machine learning algorithms to establish behavioral baselines across:
-
User login patterns
-
API usage
-
Network traffic flows
-
Data access behaviors
-
Workload communication
When deviations occur—such as unusual login times, abnormal data transfers, or privilege escalation—AI flags these as anomalies.
Unlike traditional threshold-based alerts, AI evaluates context, probability, and historical patterns, significantly reducing false positives.
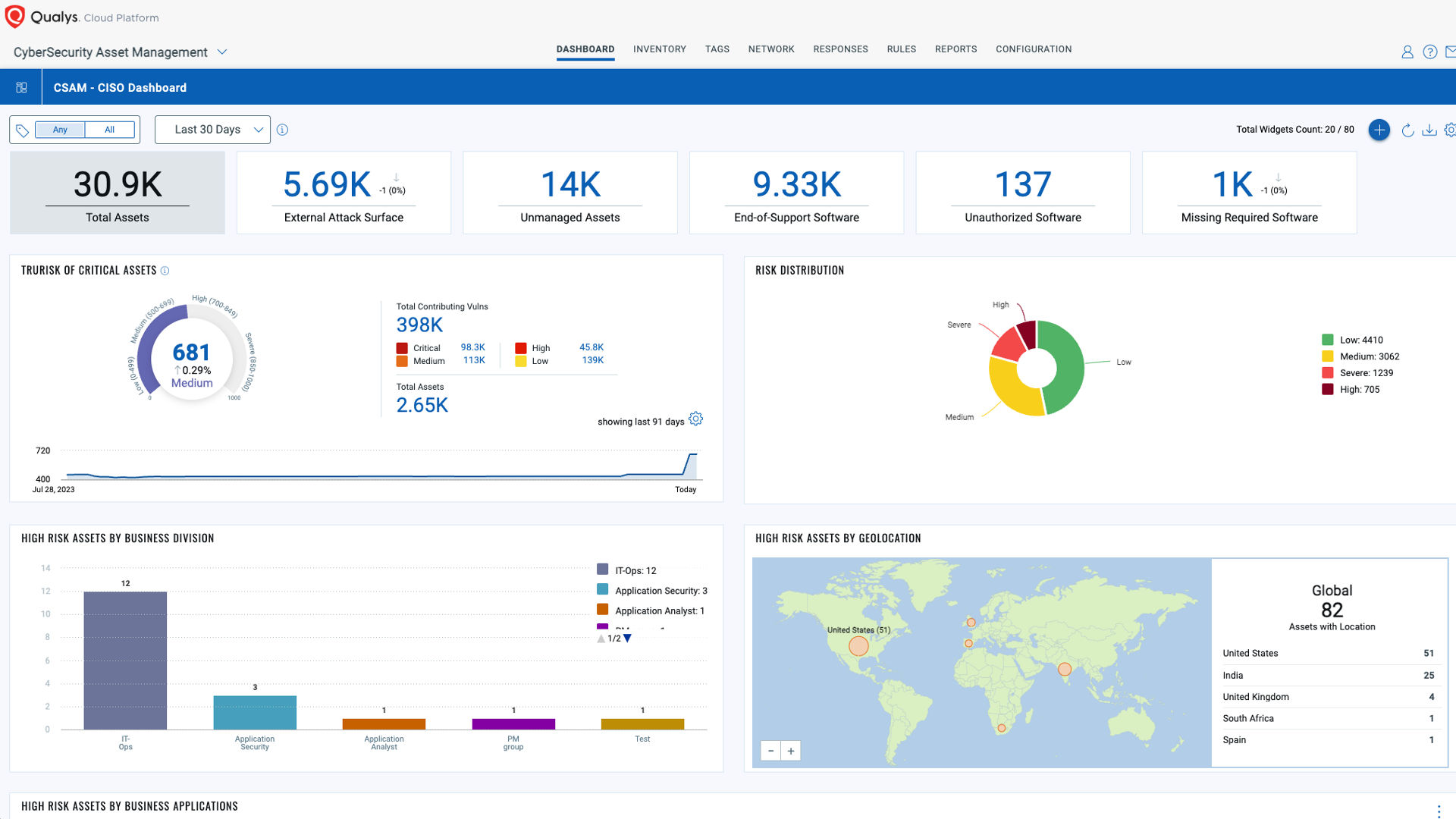
Real-Time Log Analysis at Scale
Cloud environments generate terabytes of logs daily. AI-driven Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems ingest and analyze this data in real time, correlating events across:
-
Virtual machines
-
Containers
-
Serverless functions
-
Identity systems
-
Cloud storage
This allows rapid detection of:
-
Lateral movement
-
Credential stuffing attacks
-
API abuse
-
Data exfiltration attempts
AI in Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity is the new perimeter in cloud computing. AI strengthens Identity and Access Management by:
-
Detecting compromised credentials
-
Identifying anomalous privilege escalation
-
Recommending least-privilege access
-
Monitoring machine-to-machine authentication
AI-driven IAM platforms continuously evaluate user behavior risk scores. If a developer account suddenly attempts mass data downloads from an unusual location, AI can trigger adaptive authentication or automatic session termination.
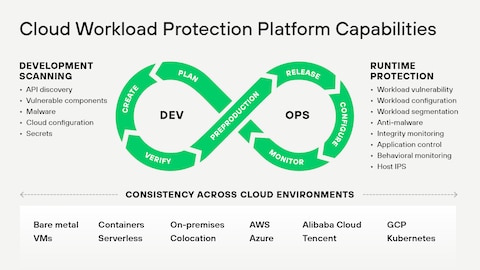
Securing Containers and Kubernetes with AI
Containerized workloads orchestrated through platforms like Kubernetes introduce additional security complexity.
AI enhances container security by:
-
Monitoring pod-to-pod communication
-
Detecting malicious container images
-
Identifying abnormal process execution
-
Preventing runtime exploits
AI-based Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) dynamically analyze container behavior instead of relying solely on static image scanning.
AI for Cloud Configuration Management
Misconfigurations remain one of the leading causes of cloud breaches. Examples include:
-
Publicly exposed storage buckets
-
Open security groups
-
Weak IAM roles
-
Improper encryption settings
AI-powered Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools:
-
Continuously scan configurations
-
Compare them against compliance frameworks
-
Predict high-risk exposure scenarios
-
Provide automated remediation recommendations
Instead of waiting for audits, AI provides continuous compliance enforcement aligned with standards such as ISO 27001, NIST, and CIS Benchmarks.
AI-Driven Incident Response and Automation
When a threat is detected, response speed determines impact.
AI-integrated Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR) platforms can:
-
Automatically isolate compromised instances
-
Revoke suspicious credentials
-
Block malicious IP addresses
-
Initiate forensic data capture
This reduces Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR), limiting damage in dynamic cloud environments.
Predictive Risk Intelligence and Threat Forecasting
AI does not only react—it predicts.
By analyzing:
-
Historical attack data
-
Global threat intelligence feeds
-
Emerging vulnerability trends
-
Cloud usage patterns
AI can forecast likely attack vectors and proactively recommend mitigation strategies. Predictive analytics enable organizations to harden high-risk assets before exploitation occurs.
AI in Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Security
Enterprises increasingly operate across multiple providers and hybrid infrastructures. AI provides unified visibility by:
-
Correlating telemetry across clouds
-
Normalizing diverse logging formats
-
Identifying cross-cloud attack patterns
-
Detecting shadow IT deployments
Without AI, achieving centralized visibility across heterogeneous environments becomes operationally overwhelming.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Cloud Security
Despite its advantages, AI adoption presents challenges:
-
Data quality issues affecting model accuracy
-
Model drift in rapidly evolving environments
-
High computational costs
-
Integration complexity with legacy systems
-
Risk of adversarial machine learning attacks
Security teams must continuously retrain models and validate outputs to maintain effectiveness.
The Future of AI in Cloud Security
Emerging trends include:
-
Autonomous cloud security operations
-
Self-healing infrastructure
-
AI-driven zero trust enforcement
-
Real-time risk scoring for workloads
-
Integration with DevSecOps pipelines
As cloud environments become more decentralized and edge-integrated, AI will serve as the control layer that maintains visibility, resilience, and policy enforcement.